Introduction
Aerodynamic drag forces on cylindrical or conical cylinder elements can be included in a Bladed calculation. The applied force is computed per unit length at both ends of the element. This article describes the force calculation used to compute the load (per unit length) at the ends of the element. The total load intensity is then computed by integrating the force per unit length at each element end across the length of the element.
This calculation is used for computation of drag load on tower elements and on the exposed section of the extender pieces linking the hub to the blade root. For computation of tower loads in the case of offshore structure the the drag loads are applied to the parts of the tower that are "dry" (in the air). If an element is part submerged then Bladed will apply drag forces to the unsubmerged sections integrating the loads between the water line and the dry end of the element.
Aerodynamic drag on element
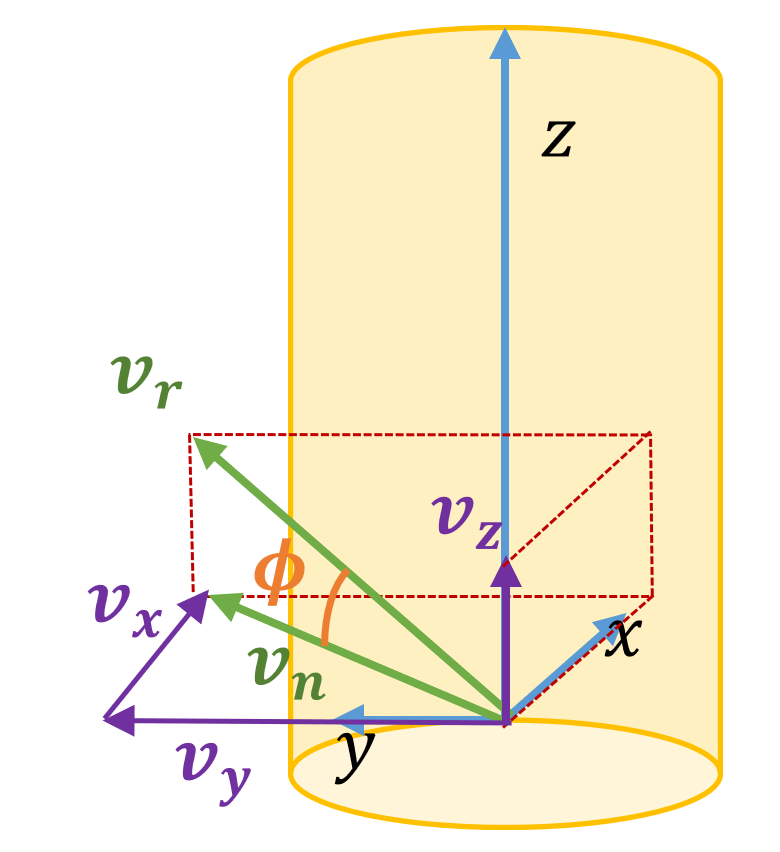
For computation of drag forces, the relative wind velocity to the element \(\bvector{v_r} = \bvector{v_a} - \bvector{v_t}\) is used to derive a component normal to the tower element axis \(\bvector{v_n} = (v_x, v_y)\). For the coordinate system used for this calculation please consult Figure 1. Note that \(\bvector{v_a}\) is the incident air velocity and \(\bvector{v_t}\) is the element structural velocity at the end of an element in the global frame. The magnitude of the component of velocity normal to the element axis is \(|\bvector{v_n}|\). The angle of incidence between \(\bvector{v_n}\) and \(\bvector{v_r}\) is denoted \(\phi\). The component of velocity parallel to the element axis \(v_z\) is not included in the computation of drag load.
The local drag force computation uses the drag coefficient \(C_d\) and the diameter \(D\) of the element end. The drag force computation is completed using the following equation:
where \(\bvector{f}= (f_x, f_y)\) is the aerodynamic drag force (per unit length) normal to the element axis.
Written in terms of the velocity \(\bvector{v_r}\) with magnitude \(|\bvector{v_r}|\) then:
which aligns with DNV RP-C205 for the calculation of drag forces due to wind loads on structures.